1. 데이터프레임에서의 데이터 선택
1) 열 선택
- 데이터프레임['컬럼이름'] 또는 데이터프레임.컬럼이름
- 데이터프레임.컬럼이름 으로 접근할 때는 컬럼이름이 반드시 문자열이어야 함
- 하나의 컬럼이름을 이용해서 접근하면 Series로 리턴
2) 행 선택
- loc[인덱스이름]
- iloc[정수형 위치 인덱스]
- Series로 리턴
3) 셀 선택
- [컬럼이름][인덱스이름]
- loc[인덱스이름, 컬럼이름]
- iloc[행 위치 인덱스, 열 위치 인덱스]
4) 다중 선택
- list를 이용해서 선택
- DataFrame이 리턴
#item.csv 파일을 읽어서 DataFrame 만들기
#csv를 읽을 때 확인할 3가지
#한글 포함 여부 - 인코딩
# 구분자는 , 인지
#첫번째 줄이 컬럼이름인지 아니면 데이터인지
#컬럼 중에 primary key의 역할을 할 수 있는게 있는지
item = pd.read_csv('./data/item.csv')
print(item.head())
item.info()| code manufacture name price 0 1 korea apple 1500 1 2 korea watermelon 15000 2 3 korea oriental melon 1000 3 4 philippines banana 500 4 5 korea lemon 1500 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> RangeIndex: 6 entries, 0 to 5 Data columns (total 4 columns): # Column Non-Null Count Dtype --- ------ -------------- ----- 0 code 6 non-null int64 1 manufacture 6 non-null object 2 name 6 non-null object 3 price 6 non-null int64 dtypes: int64(2), object(2) memory usage: 324.0+ bytes |
#현재 사용 중인 컬럼을 인덱스로 활용
item.index = item['code']item.index = ['사과', '수박', '참외', '바나나', '레몬', '망고']
print(item)| code manufacture name price 사과 1 korea apple 1500 수박 2 korea watermelon 15000 참외 3 korea oriental melon 1000 바나나 4 philippines banana 500 레몬 5 korea lemon 1500 망고 6 korea mango 700 |
#열 하나 선택
print(item['name'])
print(item.price)
print(item[['name']])
#type
print(type(item['name']))
print(type(item[['name']]))| 사과 apple 수박 watermelon 참외 oriental melon 바나나 banana 레몬 lemon 망고 mango Name: name, dtype: object 사과 1500 수박 15000 참외 1000 바나나 500 레몬 1500 망고 700 Name: price, dtype: int64 name 사과 apple 수박 watermelon 참외 oriental melon 바나나 banana 레몬 lemon 망고 mango <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'> <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> |
#여러 열 선택
print(item[['name', 'price']])| name price 사과 apple 1500 수박 watermelon 15000 참외 oriental melon 1000 바나나 banana 500 레몬 lemon 1500 망고 mango 700 |
#행선택
print(item.iloc[0]) #0번째 행
print(item.loc['apple']) #사과라는 인덱스를 가진 행| code 1 manufacture korea name apple price 1500 Name: 사과, dtype: object |
#셀선택
print(item['name'][2]) #name 컬럼의 3번째 데이터| oriental melon |
5) 범위를 이용한 행 인덱싱
[시작위치 : 종료위치 : 간격]
print(item.iloc[1:4]) #위치 인덱스에서는 마지막 위치가 포함되지 않음
print(item.loc["수박":"바나나"]) #이름 인덱스 에서는 마지막 위치가 포함됨| code manufacture name price 수박 2 korea watermelon 15000 참외 3 korea oriental melon 1000 바나나 4 philippines banana 500 code manufacture name price 수박 2 korea watermelon 15000 참외 3 korea oriental melon 1000 바나나 4 philippines banana 500 |
6) Boolean 인덱싱
- bool 타입의 Seriest를 대입하면 True 인 행 만 선택
- Series객체 비교연산자 값 이용하면 bool 타입의 Series를 리턴
- item['price'] > 3000: price 가 3000 이하이면 False 3000 초과면 True를 리턴
- & 와 | 를 이용한 결합도 가능
#price가 1500 미만인 행만 추출
print(item[item['price'] < 1500])
#price가 1000 ~ 1500 인 데이터만 추출
print(item[(item['price']>=1000) & (item['price'] <= 1500)])| code manufacture name price 참외 3 korea oriental melon 1000 바나나 4 philippines banana 500 망고 6 korea mango 700 code manufacture name price 사과 1 korea apple 1500 참외 3 korea oriental melon 1000 레몬 5 korea lemon 1500 |
- isin([데이터 나열]): 데이터 안에 속하면 True 그렇지 않으면 False를 리턴
#price 가 1000 또는 500 인 데이터 추출
print(item[item['price'].isin([1000, 500])])| code manufacture name price 참외 3 korea oriental melon 1000 바나나 4 philippines banana 500 |
2. 내용 확인
1) head 와 tail
- DataFrame의 데이터 중에서 앞 이나 뒤에서 몇 개의 데이터를 확인하고자 할 때 사용
2) shape
- 행과 열의 개수를 tuple 형식으로 리턴
3) info()
- DataFrame의 기본 정보를 리턴하는 함수
- 데이터 유형
- 행 인덱스의 구성
- 열 이름
- 각 열의 자료형 과 데이터 개수
- 메모리 사용량
4) dtypes
- 각 열의 자료형 정보를 리턴
5) count()
- 데이터의 개수
6) value_counts()
- Series에서만 사용이 가능한데 고유한 값의 종류 와 개수 정보
7) describe()
- 기술 통계 정보를 출력
- 옵션이 없으면 숫자 데이터의 평균, 표준 편차, 최대값, 최소값, 중간값
- include='all' 옵션으로 추가하면 숫자 데이터가 아닌 열의 unique, top, freq 를 출력
8) auto-mpg.csv 파일의 데이터 확인
- 자동차 연비 와 관련된 데이터 셋으로 회귀에 사용
- 컬럼
- mpg: 연비
- cylinders: 실린더 개수
- displacement: 배기량
- horsepower: 출력
- weight: 중량
- acceleration: 가속 능력
- model_year: 출시 년도
- origin: 제조국
- name: 모델명
- 데이터 확인
#헤더가 없어서 컬럼 이름을 직접 설정
df = pd.read_csv('./data/auto-mpg.csv', header=None)
df.columns = ['mpg', 'cylinders', 'displacement', 'horsepower', 'weight', 'acceleration', 'model year', 'origin', 'name']
#처음 5개의 데이터만 확인
print(df.head())| mpg cylinders displacement horsepower weight acceleration model year \ 0 18.0 8 307.0 130.0 3504.0 12.0 70 1 15.0 8 350.0 165.0 3693.0 11.5 70 2 18.0 8 318.0 150.0 3436.0 11.0 70 3 16.0 8 304.0 150.0 3433.0 12.0 70 4 17.0 8 302.0 140.0 3449.0 10.5 70 origin name 0 1 chevrolet chevelle malibu 1 1 buick skylark 320 2 1 plymouth satellite 3 1 amc rebel sst 4 1 ford torino |
#행 과 열의 수 확인
print(df.shape)
#자료형 확인
print(df.dtypes)
#데이터 개수
print(df.count())| (398, 9) mpg float64 cylinders int64 displacement float64 horsepower object weight float64 acceleration float64 model year int64 origin int64 name object dtype: object mpg 398 cylinders 398 displacement 398 horsepower 398 weight 398 acceleration 398 model year 398 origin 398 name 398 dtype: int64 |
#앞의 3가지 정보를 전부 확인 가능하고 null(None)도 확인 가능
df.info()
#기술 통계 확인 - 숫자 데이터의 기술 통계
print(df.describe())
#기술 통계 확인 - 모든 데이터의 기술 통계
print(df.describe(include='all'))| <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> RangeIndex: 398 entries, 0 to 397 Data columns (total 9 columns): # Column Non-Null Count Dtype --- ------ -------------- ----- 0 mpg 398 non-null float64 1 cylinders 398 non-null int64 2 displacement 398 non-null float64 3 horsepower 398 non-null object 4 weight 398 non-null float64 5 acceleration 398 non-null float64 6 model year 398 non-null int64 7 origin 398 non-null int64 8 name 398 non-null object dtypes: float64(4), int64(3), object(2) memory usage: 28.1+ KB mpg cylinders displacement weight acceleration \ count 398.000000 398.000000 398.000000 398.000000 398.000000 mean 23.514573 5.454774 193.425879 2970.424623 15.568090 std 7.815984 1.701004 104.269838 846.841774 2.757689 min 9.000000 3.000000 68.000000 1613.000000 8.000000 25% 17.500000 4.000000 104.250000 2223.750000 13.825000 50% 23.000000 4.000000 148.500000 2803.500000 15.500000 75% 29.000000 8.000000 262.000000 3608.000000 17.175000 max 46.600000 8.000000 455.000000 5140.000000 24.800000 model year origin count 398.000000 398.000000 mean 76.010050 1.572864 std 3.697627 0.802055 min 70.000000 1.000000 25% 73.000000 1.000000 50% 76.000000 1.000000 75% 79.000000 2.000000 max 82.000000 3.000000 mpg cylinders displacement horsepower weight \ count 398.000000 398.000000 398.000000 398 398.000000 unique NaN NaN NaN 94 NaN top NaN NaN NaN 150.0 NaN freq NaN NaN NaN 22 NaN mean 23.514573 5.454774 193.425879 NaN 2970.424623 std 7.815984 1.701004 104.269838 NaN 846.841774 min 9.000000 3.000000 68.000000 NaN 1613.000000 25% 17.500000 4.000000 104.250000 NaN 2223.750000 50% 23.000000 4.000000 148.500000 NaN 2803.500000 75% 29.000000 8.000000 262.000000 NaN 3608.000000 max 46.600000 8.000000 455.000000 NaN 5140.000000 acceleration model year origin name count 398.000000 398.000000 398.000000 398 unique NaN NaN NaN 305 top NaN NaN NaN ford pinto freq NaN NaN NaN 6 mean 15.568090 76.010050 1.572864 NaN std 2.757689 3.697627 0.802055 NaN min 8.000000 70.000000 1.000000 NaN 25% 13.825000 73.000000 1.000000 NaN 50% 15.500000 76.000000 1.000000 NaN 75% 17.175000 79.000000 2.000000 NaN max 24.800000 82.000000 3.000000 NaN |
3. DataFrame 이름변경
1) rename()
- 인덱스나 컬럼의 이름을 변경하고자할 때 사용
- index: 딕셔너리 형태로 {기존 인덱스 : 새로운 인덱스, ...} 설정
- index 변경은 메소드를 이용 X
- list나 Series 형태로 설정 가능
- Columns: 딕셔너리 형태로 {기존 컬럼 이름 : 새로운 컬럼 이름, ...} 설정하면 컬럼 이름 변경
- inplace: 이 옵션의 기본값은 False 인데 False 가 설정되면 복제본을 만들어서 리턴하고 True를 설정하면 원본이 변경
- rename: 함수는 첫번째 매개변수로 변환 함수를 대입하고 두번째 옵션에 axis 에 index 나 columns를 설정해서 변환 함수를 이용해서 변경하는 것도 가능
# 컬럼 이름 변경
import pandas as pd
item = pd.read_csv('./data/item.csv')
item.rename(columns={"code":"코드", "manufacture":"원산지", "name":"이름", "price":"가격"})
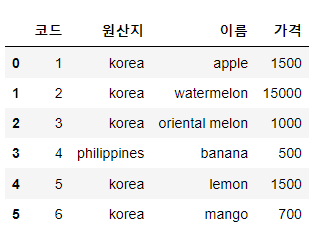 |
- 만약에 아래와 같이 한다면 아무 일도 일어나지 않는다.
names = {"code":"코드", "manufacture":"원산지", "name":"이름", "price":"가격"}
item.rename(columns=names)
#아무 일도 일어나지 않는다
#numpy나 pandas의 대다수 메소드는 원본을 변경하지 않고 수정해서 리턴- 원본을 수정할 때 inplace 옵션 사용
item.rename(columns=names, inplace=True)
#inplace 옵션이 있는지 확인하고 True로 해주면 원본을 수정
2) 인덱스의 재구성
- 인덱스
- 행을 구별하기 위한 이름
- 의미있는 이름을 인덱스로 설정
- 관계형 데이터베이스에서 기본키처럼 데이터 식별이 가능한 값
- 기본값은 0부터 일련번호
- index: 데이터 프레임 생성하면서 인덱스 지정
- reindex: index를 재배치, 추가, 삭제 가능
- set_index(열이름 or 열이름 나열): 컬럼을 인덱스로 사용하는 것이 가능, 컬럼 중에서는 제거
- reset_index(): 기본 인덱스 제거, 0부터 시작하는 일련번호 다시 부여. 피봇 형태에서 많이 사용
index 옵션 활용
# item에서 '코드'를 가져와서 인덱스로 설정, 컬럼으로 존재
item.index = item.코드
print(item)| 코드 원산지 이름 가격 코드 1 1 korea apple 1500 2 2 korea watermelon 15000 3 3 korea oriental melon 1000 4 4 philippines banana 500 5 5 korea lemon 1500 6 6 korea mango 700 |
set_index 옵션 활용
#컬럼에서 제거되고 index로 설정
item.set_index("코드")
print(item.set_index("코드"))| 원산지 이름 가격 코드 1 korea apple 1500 2 korea watermelon 15000 3 korea oriental melon 1000 4 philippines banana 500 5 korea lemon 1500 6 korea mango 700 |
reset_index 옵션 활용
item = item.reset_index()
print(item)| 코드 원산지 이름 가격 0 1 korea apple 1500 1 2 korea watermelon 15000 2 3 korea oriental melon 1000 3 4 philippines banana 500 4 5 korea lemon 1500 5 6 korea mango 700 |
2. 데이터 삭제
1) drop
- 행이나 열을 삭제
- 인덱스나 컬럼 이름을 하나 또는 list 형태로 대입
- axis=0 : 행 제거
- axis=1 : 열 제거
- inplace 옵션 존재 추천 X
#2행 삭제
print(item.drop([1], axis=0))
#code 열 삭제
print(item.drop(['code'], axis=1))
2) del
- 컬럼 제거 del DataFrame이름['컬럼이름'] 추천 X
- 다른 변수에 수정한 값을 넣으면, 원본을 보존할 수 있음
3. 데이터 수정 및 추가
- 컬럼 이름이나 인덱스는 유일무이
- DataFrame은 dict처럼 동작
DataFrame[컬럼이름] = 데이터
- 데이터를 대입할 때 하나의 값이나 Vector 데이터 (list, ndarray, Series, dict) 사용
- 행 수정 및 추가
DataFrame.loc[인덱스이름] = 데이터
- 인덱스 이름이 존재하지 않으면 추가, 인덱스 이름이 존재하면 수정!
# 하나의 값을 설정하면 모든 행 값이 동일한 값으로 대입
item['description'] = '과일'
print(item)| code manufacture name price description 0 1 korea apple 1500 과일 1 2 korea watermelon 15000 과일 2 3 korea oriental melon 1000 과일 3 4 philippines banana 500 과일 4 5 korea lemon 1500 과일 5 6 korea mango 700 과일 |
# dict를 이용하면 key와 index가 일치할 때 값을 대입
item['description'] = ['사과', '수박', '참외', '바나나', '레몬', '망고']
print(item)| code manufacture name price description 0 1 korea apple 1500 사과 1 2 korea watermelon 15000 수박 2 3 korea oriental melon 1000 참외 3 4 philippines banana 500 바나나 4 5 korea lemon 1500 레몬 5 6 korea mango 700 망고 |
# 컬럼 수정 - Series나 dict는 인덱스나 키 이름대로 대입
item['description'] = {0:'사과', 1:'수박', 2:'딸기', 5:'포도', 4:'바나나', 3:'망고'}
print(item)| code manufacture name price description 0 1 korea apple 1500 사과 1 2 korea watermelon 15000 수박 2 3 korea oriental melon 1000 딸기 3 4 philippines banana 500 망고 4 5 korea lemon 1500 바나나 5 6 korea mango 700 포도 |
# 행 추가
item.loc[6] = [7, '한국', '무화과', 3000, '무화과']
print(item)| code manufacture name price description 0 1 korea apple 1500 사과 1 2 korea watermelon 15000 수박 2 3 korea oriental melon 1000 딸기 3 4 philippines banana 500 망고 4 5 korea lemon 1500 바나나 5 6 korea mango 700 포도 6 7 한국 무화과 3000 무화과 |
# 특정 셀 수정
item.loc[6, 'name'] = "fig"
print(item)| code manufacture name price description 0 1 korea apple 1500 사과 1 2 korea watermelon 15000 수박 2 3 korea oriental melon 1000 딸기 3 4 philippines banana 500 망고 4 5 korea lemon 1500 바나나 5 6 korea mango 700 포도 6 7 한국 fig 3000 무화과 |
4. 연산
1) 전치 연산
- 행과 열을 전환하는 연산
- T 속성 이용
- transpose() 함수 이용
2) 산술 연산
- numpy와 동일한 방식으로 연산 수행 (브로드캐스트 연산)
- numpy는 위치 기반으로 연산을 수행하지만, Series나 DataFrame은 인덱스 기반으로 연산수행
- 한쪽에만 존재하는 경우 NaN으로 결과 설정
- 산술 연산자 사용 가능
- add, sub, div, mul 메소드 이용 가능. fill_value 옵션에 한쪽에만 존재하는 인덱스에 기본값 설정
item1 = {
"1":{'price':1000},
"2":{'price':2000}
}
item2 = {
"1":{'price':1000},
"3":{'price':3000}
}
df1 = pd.DataFrame(item1).T
df2 = pd.DataFrame(item2).T| price 1 1000 2 2000 price 1 1000 3 3000 |
# 브로드캐스트 연산
print(df1 + 200) #200을 df1의 개수만큼 복제해서 연산| price 1 1200 2 2200 |
# 데이터프레임끼리 산술 연산
print(df1 + df2)| price 1 2000.0 2 NaN 3 NaN |
- 존재하지 않는 인덱스 결과는 Nan(None과 조금 다름)
# 함수 사용 연산
print(df1.add(df2, fill_value=0))| price 1 2000.0 2 2000.0 3 3000.0 |
- 한쪽에만 존재하는 인덱스에 기본값 설정해서 연산 수행
# 행 단위 연산
print(df1.add(df2, axis=0))| price 1 2000.0 2 NaN 3 NaN |
3) 기본 통계 함수
- count, min, max, sum, mean, median, mode(최빈값)
- var(분산), std(표준 편차), kurt(첨도), skew(왜도), sem(평균의 표준 오차)
- argmin, argmax, dixmin, dixmax
- quantile(4분위수)
- describe(기술 통계 정보 요약)
- cumsum, cummin, cummax, cumprod: 누적합, 누적최소, 누적최대, 누적곱
- diff(산술적인 차이)
- pct_change(이전 데이터와의 백분율)
- unique(): Series에서만 사용 가능한데 동일한 값을 제외한 데이터의 배열 리턴하는 데 skipna 옵션을 이용해서 NaN 제거 가능
mpg = pd.read_csv("./data/auto-mpg.csv", header=None)
mpg.columns = ['mpg', 'cylinders', 'displacement', 'horsepower', 'weight',
'acceleration', 'model year', 'origin', 'name']
print(mpg.head())| mpg cylinders displacement horsepower weight acceleration model year \ 0 18.0 8 307.0 130.0 3504.0 12.0 70 1 15.0 8 350.0 165.0 3693.0 11.5 70 2 18.0 8 318.0 150.0 3436.0 11.0 70 3 16.0 8 304.0 150.0 3433.0 12.0 70 4 17.0 8 302.0 140.0 3449.0 10.5 70 origin name 0 1 chevrolet chevelle malibu 1 1 buick skylark 320 2 1 plymouth satellite 3 1 amc rebel sst 4 1 ford torino |
# 기술 통계 함수
print(mpg[['mpg']].mean())
print(mpg[['mpg', 'weight']].mean())| mpg 23.514573 dtype: float64 mpg 23.514573 weight 2970.424623 dtype: float64 |
# describe()
print(mpg.describe())| mpg cylinders displacement weight acceleration \ count 398.000000 398.000000 398.000000 398.000000 398.000000 mean 23.514573 5.454774 193.425879 2970.424623 15.568090 std 7.815984 1.701004 104.269838 846.841774 2.757689 min 9.000000 3.000000 68.000000 1613.000000 8.000000 25% 17.500000 4.000000 104.250000 2223.750000 13.825000 50% 23.000000 4.000000 148.500000 2803.500000 15.500000 75% 29.000000 8.000000 262.000000 3608.000000 17.175000 max 46.600000 8.000000 455.000000 5140.000000 24.800000 model year origin count 398.000000 398.000000 mean 76.010050 1.572864 std 3.697627 0.802055 min 70.000000 1.000000 25% 73.000000 1.000000 50% 76.000000 1.000000 75% 79.000000 2.000000 max 82.000000 3.000000 |
- 무의미한 컬럼(origin)의 기술통계가 같이 구해짐
mpg['origin'] = mpg['origin'].astype('str')
print(mpg.describe())- 형변환 해주기!
4) 상관관계 파악
- 상관관계: 2개의 데이터의 동일한 또는 반대되는 경향을 갖는 관계
- 상관관계가 높다는 것은 동일한 경항 또는 완전히 반대되는 경향을 갖는 경우
- cov(): 공분산
- 거리의 제곱
- corr(): 상관계수
- 공분산과 데이터의 스케일을 맞추지 않고 모든 값이 동일한 스케일을 갖도록 값을 수정
- -1 ~ 1이 되도록 수정
- 절대값 1에 가까워지면 상관관계가 높고, 0에 가까워지면 상관관계가 낮음
print(mpg[['mpg', 'cylinders', 'displacement']].corr())| mpg cylinders displacement mpg 1.000000 -0.775396 -0.804203 cylinders -0.775396 1.000000 0.950721 displacement -0.804203 0.950721 1.000000 |
5) 정렬
- 인덱스나 컬럼 이름에 따른 정렬
- sort_index() 메소드 이용
- 기본은 인덱스가 기준
- 오름차순이 기본. 내림차순을 할 때는 ascending = False 설정
- axis=1 : 컬럼 이름을 기준으로 정렬 수행
- 컬럼의 값을 기준으로 정렬
- sort_values(by = 열 이름 또는 열 이름의 list, ascending=bool 또는 bool의 list)
6) 순위
- rank 함수 이용
- 기본 오름차순
- ascending = False 내림차순
- axis로 행 열 단위 설정
- 동일한 점수가 있는 경우 기본적으로 순위의 평균 리턴
- method 옵션에 max, min, first 설정해서 동일한 점수 처리하는 것이 가능
- 순위는 컬럼 단위로 연산 수행
- 컬럼의 개수가 2개면 순위도 2개 리턴
#내림차순
print(mpg.sort_values(by=['mpg'], ascending=[False]))| mpg cylinders displacement horsepower weight acceleration \.... 322 46.6 4 86.0 65.00 2110.0 17.9 329 44.6 4 91.0 67.00 1850.0 13.8 325 44.3 4 90.0 48.00 2085.0 21.7 394 44.0 4 97.0 52.00 2130.0 24.6 326 43.4 4 90.0 48.00 2335.0 23.7 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... |
#오름차순
print(mpg.sort_values(by=['mpg', 'displacement'], ascending=[True, True]))| mpg cylinders displacement horsepower weight acceleration \ 28 9.0 8 304.0 193.0 4732.0 18.5 26 10.0 8 307.0 200.0 4376.0 15.0 25 10.0 8 360.0 215.0 4615.0 14.0 27 11.0 8 318.0 210.0 4382.0 13.5 124 11.0 8 350.0 180.0 3664.0 11.0 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... |
#동일한 값은 순위의 평균
print(mpg.rank())| mpg cylinders displacement horsepower weight acceleration \ 0 116.0 347.0 324.0 74.0 290.0 36.5 1 61.5 347.0 352.5 132.5 309.0 27.0 2 116.0 347.0 334.0 111.5 284.0 15.0 3 81.0 347.0 315.0 111.5 283.0 36.5 4 96.0 347.0 306.0 87.0 287.0 11.0 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... |
- .5는 같은 값이 2개라는 거
#동일한 값은 낮은 순위 부여
print(mpg.rank(method='min'))| mpg cylinders displacement horsepower weight acceleration \ 0 108.0 296.0 323.0 72.0 290.0 32.0 1 54.0 296.0 344.0 131.0 309.0 24.0 2 108.0 296.0 326.0 101.0 284.0 12.0 3 75.0 296.0 312.0 101.0 283.0 32.0 4 93.0 296.0 301.0 84.0 287.0 11.0 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... |

'Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] 데이터 전처리 (0) | 2024.02.15 |
|---|---|
| [Python] 데이터 시각화 (0) | 2024.02.14 |
| [Python] MySQL 데이터로 DataFrame 만들기 (0) | 2024.02.14 |
| [Python] 크롤링 - Selenium (0) | 2024.02.14 |
| [Python] 크롤링 - 기사 스크래핑 (0) | 2024.02.14 |
